1.Driving Belt.
The transmission belt is a belt used to transmit mechanical power, consisting of rubber and reinforcing materials such as cotton canvas, synthetic fibers, synthetic fibers, or steel wire. It is made by laminating rubber canvas, synthetic fiber fabric, curtain wire, and steel wire as tensile layers, and then forming and vulcanizing it. It is widely used in the power transmission of various machinery.
● V belt
The V-belt has a trapezoidal cross-section and consists of four parts: the fabric layer, the bottom rubber, the top rubber, and the tensile layer. The fabric layer is made of rubber canvas and serves a protective function; the bottom rubber is made of rubber and withstands compression when the belt is bent; the top rubber is made of rubber and withstands tension when the belt is bent; the tensile layer is composed of several layers of fabric or impregnated cotton cord, bearing the basic tensile load.

● Flat belt
The flat belt has a rectangular cross-section, with the inner surface serving as the working surface. There are various types of flat belts, including rubber canvas flat belts, woven belts, cotton-reinforced composite flat belts, and high-speed circular belts. The flat belt has a simple structure, convenient transmission, is not limited by distance, and is easy to adjust and replace. The transmission efficiency of flat belts is low, generally around 85%, and they occupy a large area. They are widely used in various industrial and agricultural machinery.
● Round belt
Round belts are transmission belts with a circular cross-section, allowing for flexible bending during operation. These belts are mostly made of polyurethane, typically without a core, making them structurally simple and easy to use. There has been a sharp increase in demand for these belts in small machine tools, sewing machines, and precision machinery.
● Synchronoud Toothed Belt
Synchronous belts typically use steel wire or glass fiber ropes as the load-bearing layer, with chloroprene rubber or polyurethane as the base. The belts are thin and light, suitable for high-speed transmission. They are available as single-sided belts (with teeth on one side) and double-sided belts (with teeth on both sides). Single-sided belts are mainly used for single-axis transmission, while double-sided belts are used for multi-axis or reverse rotation.
● Poly V-Belt
The poly V-belt is a circular belt with several longitudinal triangular wedges on the base of the rope core flat belt. The working surface is the wedge surface, and it is made of rubber and polyurethane. Due to the elastic teeth on the inner side of the belt, it can achieve non-slip synchronous transmission, and has the characteristics of being lighter and quieter than chains.
2.Driving Pulley
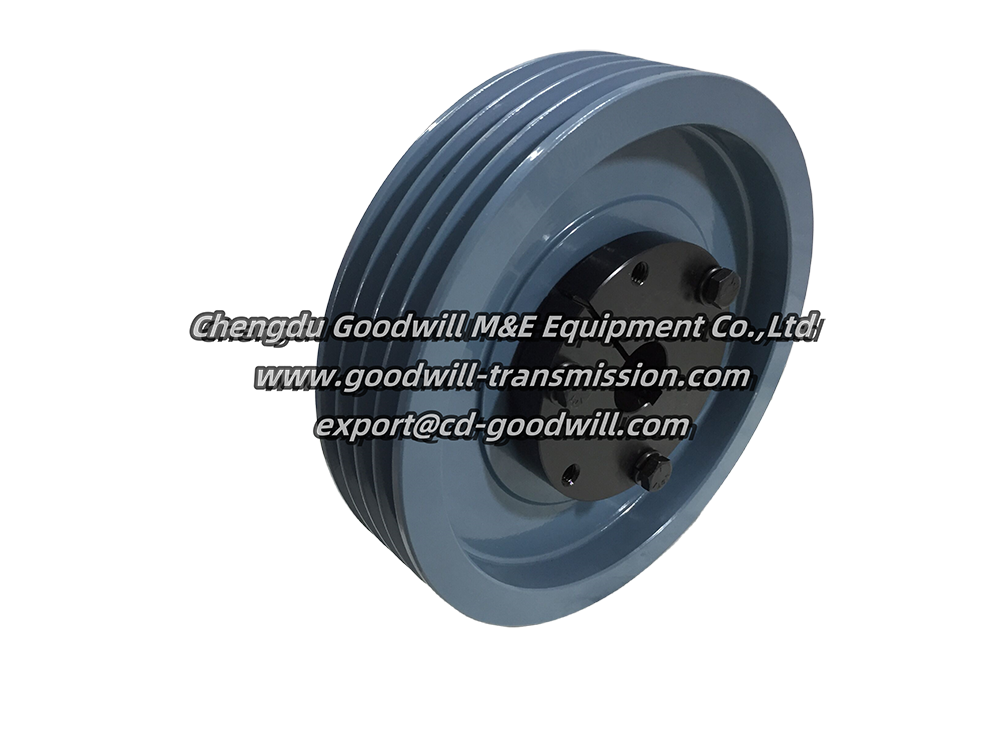
● V-belt pulley
The V-belt pulley consists of three parts: the rim, the spokes, and the hub. The spoke section includes solid, spoked, and elliptical spokes. Pulleys are commonly made of cast iron, and sometimes steel or non-metallic materials (plastic, wood) are used. Plastic pulleys are lightweight and have a high coefficient of friction, and are often used in machine tools.
● Web pulley
When the pulley diameter is less than 300mm, a web type can be used.
● Orifice pulley
When the pulley diameter is less than 300mm and the outer diameter minus the inner diameter is greater than 100mm, a orifice type can be used.
● Flat belt pulley
The material of the flat belt pulley is mainly cast iron, cast steel is used for high speed, or steel plate is stamped and welded, and cast aluminum or plastic can be used for low power situation. To prevent belt slippage, the surface of the large pulley rim is usually made with a convexity.
● Synchronous toothed-belt pulley
The tooth profile of the synchronous toothed belt pulley is recommended to be involute, which can be machined by the generating method, or straight tooth profile can also be used.
Post time: Jul-15-2024




